Choose the true statements about amyloid fibrils – Amyloid fibrils, enigmatic protein aggregates, have captivated the scientific community with their complex structure and diverse biological roles. This article delves into the fascinating world of amyloid fibrils, exploring their formation, properties, and implications in health and disease.
From their unique cross-beta sheet architecture to their involvement in neurodegenerative disorders, amyloid fibrils present a compelling subject for scientific inquiry. This guide unravels the intricate tapestry of amyloid fibril biology, providing a comprehensive understanding of these enigmatic structures.
1. Definition of Amyloid Fibrils
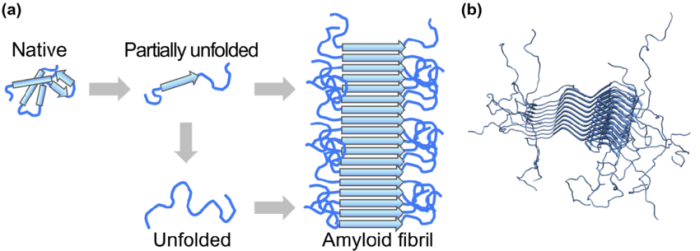
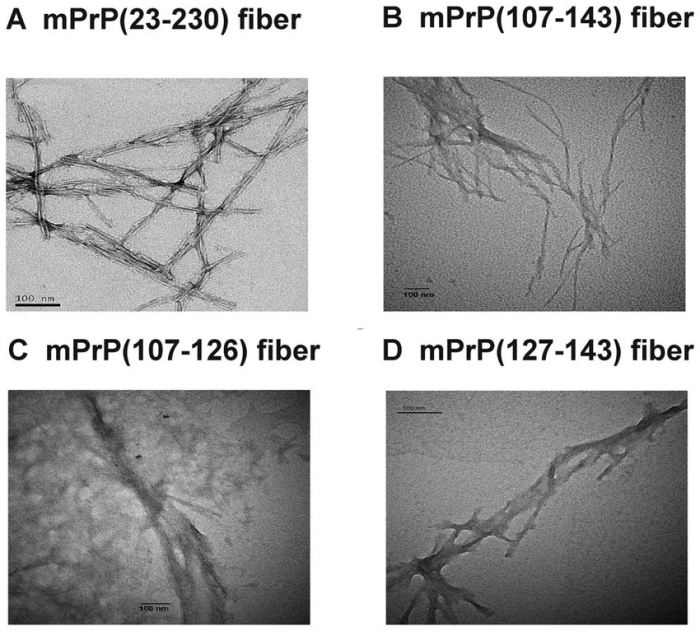
Amyloid fibrils are highly ordered protein aggregates that exhibit a characteristic cross-beta sheet structure. They are distinct from other protein aggregates due to their unique structural properties, stability, and resistance to degradation.
Molecularly, amyloid fibrils are composed of polypeptide chains arranged in a parallel, in-register manner. The beta-strands run perpendicular to the fibril axis, forming a stable cross-beta sheet architecture. This structural arrangement gives amyloid fibrils their characteristic rigidity and insolubility.
2. Formation and Assembly
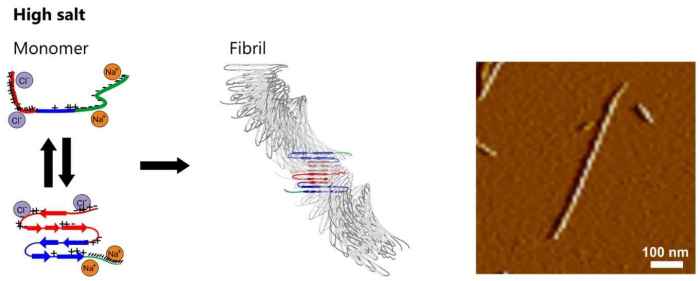
Amyloid fibril formation is a complex process that involves several steps. It typically begins with the misfolding or partial unfolding of a protein, exposing hydrophobic regions that would normally be buried within the native structure. These exposed hydrophobic regions interact with each other, leading to the formation of oligomeric intermediates.
Over time, these oligomers can aggregate and align to form protofibrils, which are precursors to mature amyloid fibrils. Protofibrils further elongate and mature into amyloid fibrils through a process known as secondary nucleation. The rate and extent of fibril assembly are influenced by various factors, including protein concentration, temperature, pH, and the presence of cofactors or inhibitors.
3. Structural Properties, Choose the true statements about amyloid fibrils
Amyloid fibrils exhibit unique structural features that distinguish them from other protein aggregates. Their cross-beta sheet architecture, formed by the parallel alignment of beta-strands, is a defining characteristic. This structural arrangement results in a highly stable and ordered fibril structure.
Amyloid fibrils are also characterized by their insolubility in water and resistance to proteolytic degradation. This stability is attributed to the extensive hydrogen bonding network within the cross-beta sheet structure and the lack of exposed hydrophobic surfaces.
Query Resolution: Choose The True Statements About Amyloid Fibrils
What are amyloid fibrils?
Amyloid fibrils are elongated, insoluble protein aggregates characterized by a unique cross-beta sheet architecture.
How do amyloid fibrils form?
Amyloid fibril formation involves a complex process of protein misfolding, aggregation, and assembly.
What are the biological roles of amyloid fibrils?
Amyloid fibrils have diverse biological roles, ranging from structural support to hormone storage.
How are amyloid fibrils involved in disease?
Amyloid fibril accumulation is associated with various diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes.
What are the current research directions on amyloid fibrils?
Ongoing research focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms of amyloid fibril formation, disease pathogenesis, and therapeutic targeting.