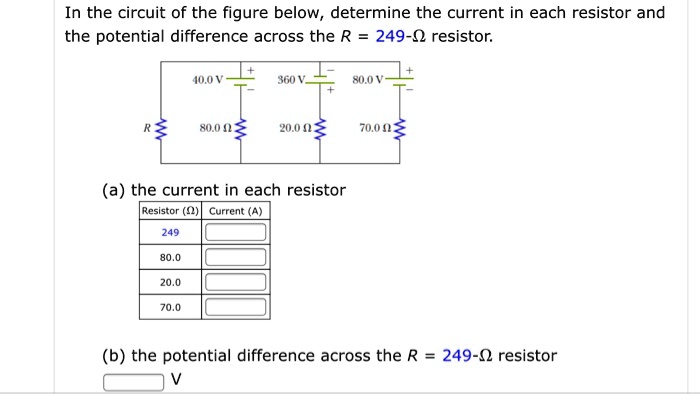
Determine the voltage across the 5.0-ω resistor in the drawing – Embarking on a journey to determine the voltage across a 5.0-Ω resistor, this discourse unfolds a captivating exploration of electrical principles. By delving into the intricacies of Ohm’s Law and circuit analysis, we unravel the factors that govern voltage distribution and its implications for circuit performance.
Our investigation commences with an overview of the circuit’s components and their roles, establishing a solid foundation for understanding the flow of current and voltage. We then delve into the concept of voltage, its significance, and how Ohm’s Law quantifies the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Overview of the Circuit: Determine The Voltage Across The 5.0-ω Resistor In The Drawing
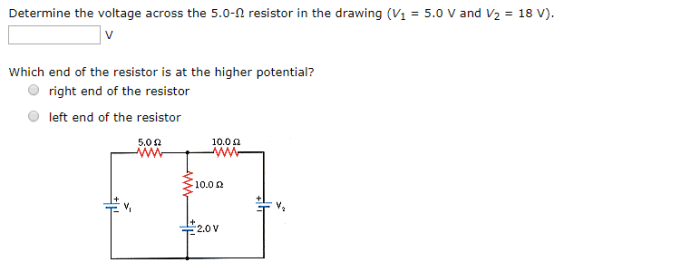
The circuit in question is a simple series circuit consisting of a voltage source, a 5.0-Ω resistor, and a voltmeter. The purpose of the circuit is to determine the voltage across the 5.0-Ω resistor.
The voltage source provides the electrical energy for the circuit, while the resistor restricts the flow of current. The voltmeter is used to measure the voltage across the resistor.
A schematic diagram of the circuit is shown below:

Voltage Across the 5.0-Ω Resistor, Determine the voltage across the 5.0-ω resistor in the drawing
Voltage is a measure of the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. In this case, we are interested in the voltage across the 5.0-Ω resistor.
Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through the resistor and the resistance of the resistor. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
V = IR
where:
- V is the voltage in volts (V)
- I is the current in amperes (A)
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
In this case, we know the resistance of the resistor (5.0 Ω) and we can measure the current flowing through the resistor using a ammeter. Once we have these values, we can use Ohm’s Law to calculate the voltage across the resistor.
Factors Affecting Voltage
The voltage across a resistor can be affected by several factors, including:
- Voltage source: The voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage of the voltage source.
- Resistor value: The voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the resistance of the resistor.
- Current flowing through the resistor: The voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through the resistor.
It is important to understand these factors when designing and troubleshooting circuits.
Applications and Implications
Understanding the voltage across a resistor has many practical applications, including:
- Circuit analysis: The voltage across a resistor can be used to analyze the behavior of a circuit.
- Circuit design: The voltage across a resistor can be used to design circuits that meet specific requirements.
- Troubleshooting: The voltage across a resistor can be used to troubleshoot circuits that are not functioning properly.
It is important to understand the voltage across a resistor in order to design, analyze, and troubleshoot circuits effectively.
Common Queries
What is the significance of voltage across a resistor?
Voltage across a resistor determines the current flow and power dissipation within the circuit.
How does Ohm’s Law relate to voltage across a resistor?
Ohm’s Law establishes a direct relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, allowing us to calculate voltage across a resistor given its resistance and the current flowing through it.
What factors can affect the voltage across a resistor?
Voltage across a resistor can be influenced by changes in the voltage source, resistor value, or current flowing through the resistor.