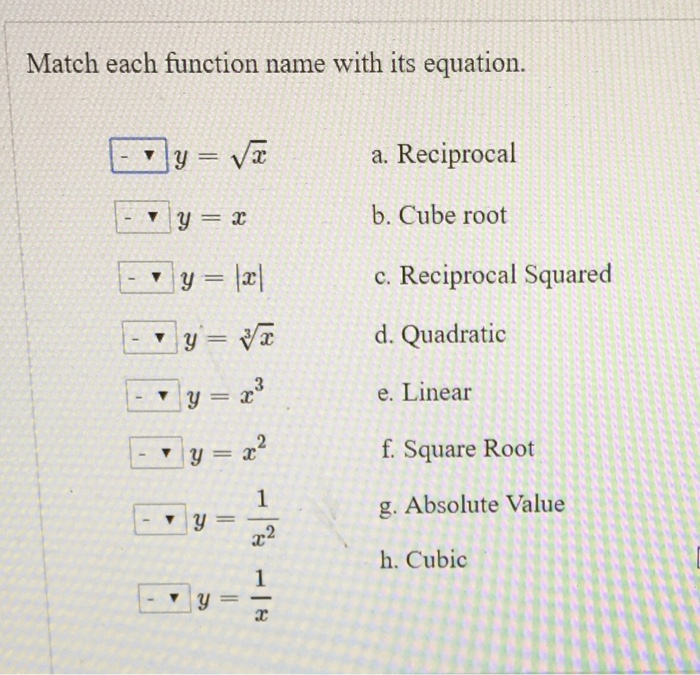
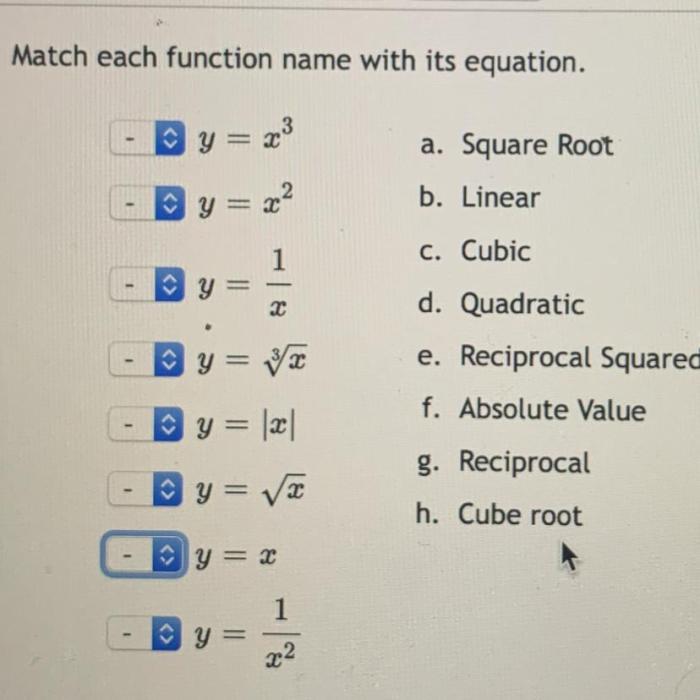
Match each function name with its equation – Matching function names with their equations is a crucial skill in mathematics, providing a foundation for understanding and applying mathematical concepts across various fields. By recognizing the relationship between function names and equations, we unlock the power to solve complex problems, model real-world phenomena, and make informed decisions.
This guide delves into the intricacies of function matching, exploring different types of functions, their equations, and their practical applications. With a comprehensive table of common function names and their corresponding equations, along with real-world examples, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the world of functions.
Function Names and Equations: Match Each Function Name With Its Equation
Matching function names with their equations is essential for understanding and utilizing mathematical functions effectively. This knowledge enables us to determine the specific mathematical operation performed by a function and apply it appropriately in various contexts.
By understanding the relationship between function names and equations, we can identify the type of function (e.g., linear, quadratic, exponential), its behavior, and the range of values it produces. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions about which functions to use for specific mathematical tasks and to interpret the results they generate.
Matching Function Names with Equations, Match each function name with its equation
The following table provides a list of common function names, their corresponding equations, brief descriptions, and examples of their usage:
| Function Name | Equation | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Function | y = mx + b | Represents a straight line with a constant slope (m) and y-intercept (b). | y = 2x + 3 |
| Quadratic Function | y = ax^2 + bx + c | Represents a parabola with a vertex and two zeros. | y = x^2
|
| Exponential Function | y = a^x | Represents a curve that increases or decreases rapidly as x changes. | y = 2^x |
| Trigonometric Function | y = sin(x), y = cos(x), y = tan(x) | Represents periodic functions that model angles and lengths in triangles. | y = sin(30°) |
Types of Functions
Functions can be categorized into different types based on their equations:
- Linear functionshave equations of the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- Quadratic functionshave equations of the form y = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants.
- Exponential functionshave equations of the form y = a^x, where a is a constant.
- Trigonometric functionshave equations of the form y = sin(x), y = cos(x), or y = tan(x), where x is an angle.
Applications of Function Matching
Matching function names with equations is a fundamental skill used in various fields:
- Science:Modeling physical phenomena, such as projectile motion or radioactive decay.
- Engineering:Designing structures, circuits, and systems.
- Finance:Analyzing financial data, forecasting market trends, and managing investments.
FAQ Summary
What are the benefits of understanding the relationship between function names and equations?
Understanding this relationship enables problem-solving, modeling of real-world phenomena, and informed decision-making.
How can I identify different types of functions based on their equations?
By analyzing the equation’s structure, such as linearity, quadratic terms, exponential growth, or trigonometric functions.
What are some real-world applications of function matching?
Function matching finds applications in science (modeling physical phenomena), engineering (design and analysis), and finance (financial modeling and forecasting).