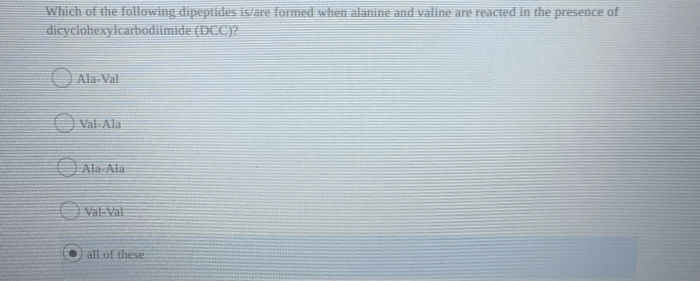
Which of the following dipeptides will be formed? This question lies at the heart of understanding dipeptide formation, a fundamental process in biochemistry. Dipeptides, composed of two amino acids linked by a peptide bond, play crucial roles in various biological processes.
This exploration delves into the intricacies of dipeptide formation, examining the factors that influence their synthesis and the methods employed for their analysis. Moreover, it highlights the diverse applications of dipeptides, showcasing their significance in fields ranging from food science to pharmaceuticals.
Dipeptide formation involves the condensation reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another, resulting in the release of a water molecule. The specific dipeptide formed depends on the amino acids involved and the conditions under which the reaction takes place.
Factors such as pH, temperature, and enzyme concentration significantly impact the rate and efficiency of dipeptide formation.
Dipeptide Formation: Which Of The Following Dipeptides Will Be Formed

Dipeptides are formed through the covalent bonding of two amino acids. The process involves the condensation reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another, resulting in the formation of an amide bond. The general equation for dipeptide formation is:
R 1-NH 2+ R 2-COOH → R 1-NH-CO-R 2+ H 2O
Where R 1and R 2represent the side chains of the two amino acids.
Examples of amino acids that can form dipeptides include:
- Glycine and alanine to form glycylalanine
- Phenylalanine and serine to form phenylalanylserine
- Aspartic acid and glutamic acid to form aspartylglutamic acid
Factors Affecting Dipeptide Formation
Several factors influence the rate and efficiency of dipeptide formation, including:
- pH:The optimal pH for dipeptide formation is typically between 7 and 9. At pH values below 7, the amino and carboxyl groups are protonated, reducing their reactivity. At pH values above 9, the hydroxide ion concentration is high, promoting the formation of amide bonds.
- Temperature:Dipeptide formation is an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases heat. Therefore, increasing the temperature typically increases the rate of dipeptide formation. However, excessively high temperatures can denature enzymes and other factors involved in the reaction.
- Enzyme concentration:Enzymes, such as proteases and peptidases, can catalyze the formation of dipeptides. Increasing the enzyme concentration can accelerate the reaction rate.
Methods for Dipeptide Analysis, Which of the following dipeptides will be formed
Various methods can be used to analyze dipeptides, including:
- Chromatography:Techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC) can separate dipeptides based on their physical and chemical properties.
- Mass spectrometry:Mass spectrometry techniques, such as matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) and electrospray ionization (ESI), can determine the molecular weight and structure of dipeptides.
Applications of Dipeptides
Dipeptides have various applications in different fields:
- Food science:Dipeptides are used as food additives to enhance flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
- Pharmaceuticals:Dipeptides can act as drugs or drug intermediates, with applications in treating conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and pain.
- Cosmetics:Dipeptides are incorporated into skincare products as anti-aging agents and moisturizers.
Questions and Answers
What factors influence dipeptide formation?
Factors such as pH, temperature, and enzyme concentration significantly impact the rate and efficiency of dipeptide formation.
What methods are used to analyze dipeptides?
Methods such as chromatography and mass spectrometry are commonly employed for dipeptide analysis, providing valuable insights into their structure and composition.
What are the applications of dipeptides?
Dipeptides find applications in various fields, including food science, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, where they play specific roles and offer unique benefits.